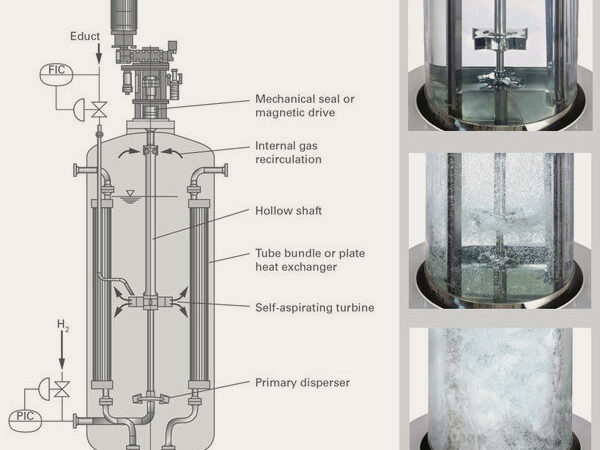
Hydrogenation
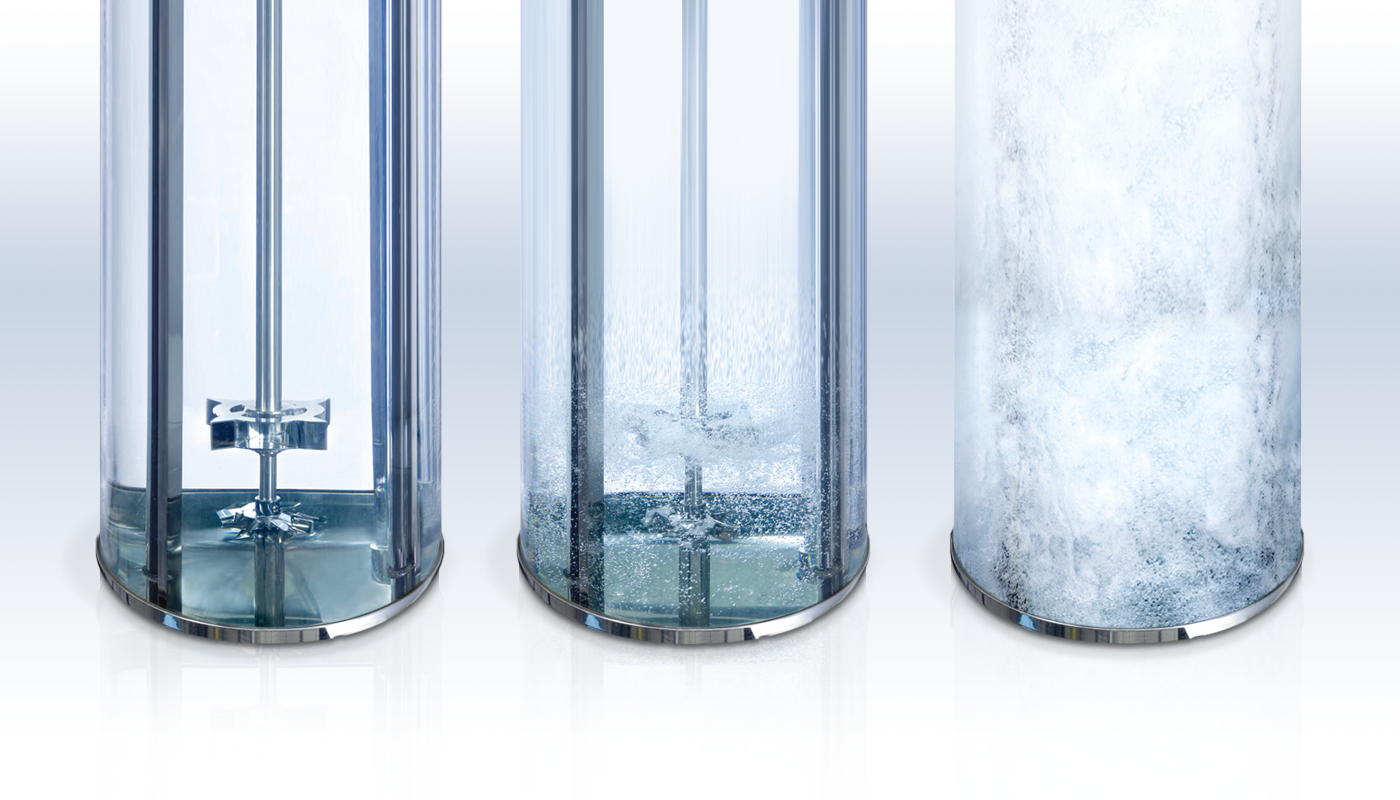
High Efficient Mass Transfer and Heat Exchange

The agitation system priarily has the following tasks
- Intensification of the mass transfer of hydrogen from the gas to the liquid phase
- Removal of the heat of reaction by flowing against the heat exchanger in the reactor
- Suspending the catalyst
- Homogenizing the reactor contents
- Avoidance of concentration and temperature differences
Hydrogenation Plants for Specialty Chemicals
A manufacturer of specialty chemicals for the paint industry was able to determine through tests in the hydrogenation pilot plant at EKATO in Schopfheim, Germany, that it is possible to reduce the catalyst loading from 2.5% to 1.0% and the reaction time from four to two hours if the dispersion of the hydrogen and the cooling capacity of the reactor are improved. The subsequent conversion of the existing hydrogenation reactor was planned and executed by EKATO in terms of process engineering and mechanics. Core elements of the rebuild were a conversion of the reactor with 2 m3 useful volume to the unique EKATO combi gassing, as well as an optimization of the existing cooling system. With 1200 starts per year, 3,600 kg of a Pd/C catalyst could be saved annually, resulting in savings in the amount of approx. 400,000.00 Euro per year.
Successful optimization of a hydrogenation reactor together with EKATO
- Annual saving of 3,600 kg Pd/C catalyst
- Savings of approx. 400,000€ per year.
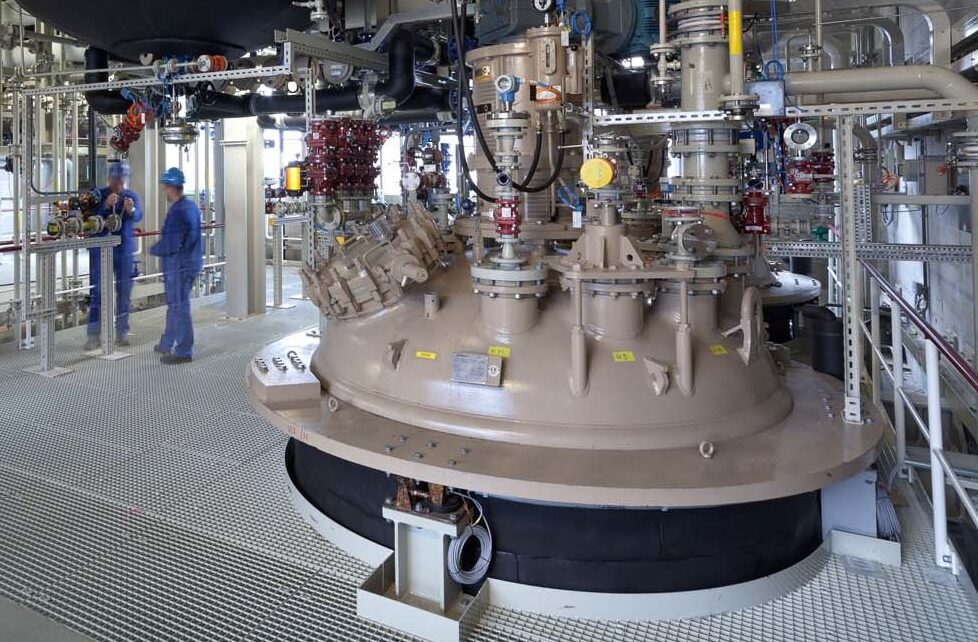

Production of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API)
The pre-qualified modules of our new hydrogenation unit were installed on the day of arrival and we started the production in the same month

Hydrogenation Plants for Sugar Alcohol
Sorbitol is a sugar alcohol obtained by hydrogenation of glucose. Sugar alcohols are used as sugar substitutes in the food industry and are also important raw materials for numerous other applications and markets. In order to ensure the best product quality with increasing demands on economic efficiency, EKATO has carried out extensive development studies to analyze and optimize the hydrogenation of sugars to sugar alcohols such as sorbitol, xylitol and mannitol. The aim of these development studies was to increase the space-time yield, minimize the content of residual reducing sugars, suppress the formation of gluconic acid, and improve the catalyst lifetime.
Based on these extensive investigations, a new, optimized standard series of hydrogenation reactors was developed for the production of sugar alcohols with filling volumes of up to 88 m3 . In addition to process engineering optimization, the new reactor series was investigated by means of FEM in order to exclude the possibility of failure of reactor internals under cyclic loads.
Most competitive hydrogenation technology for polyol derivates
- High performance reactor technology
- Robust and reliable equipment
- Low capital expenses
- Low operating expenses